Basics of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds have emerged as a favored investment avenue for individuals seeking to grow their Wealth without the intricacies of picking individual stocks or bonds. They offer a simplified, professionally managed way to invest across different asset classes, making them ideal for both beginners and seasoned investors.
Whether you’re saving for retirement, planning a major purchase, or aiming for consistent income, having a firm grasp of how mutual funds work is crucial for making smart investment choices.
In this article, we’ll break down the fundamentals of mutual funds, including what they are, the types available, their advantages and risks, and how to start investing.
What Are Mutual Funds?
A Mutual Fund pools money from multiple investors and invests it in a Diversified Portfolio of assets like stocks, bonds, or other Securities. Investors hold units of the fund, not the actual underlying assets. These funds are overseen by professional fund managers who aim to meet the fund’s investment goals through strategic allocation of the portfolio.
How Do Mutual Funds Work?
When you invest in a mutual fund, you purchase units at the fund’s Net Asset Value (NAV), which changes daily based on the value of its Holdings. Returns can be in the form of dividends, interest, or Capital Gains generated from the investments.
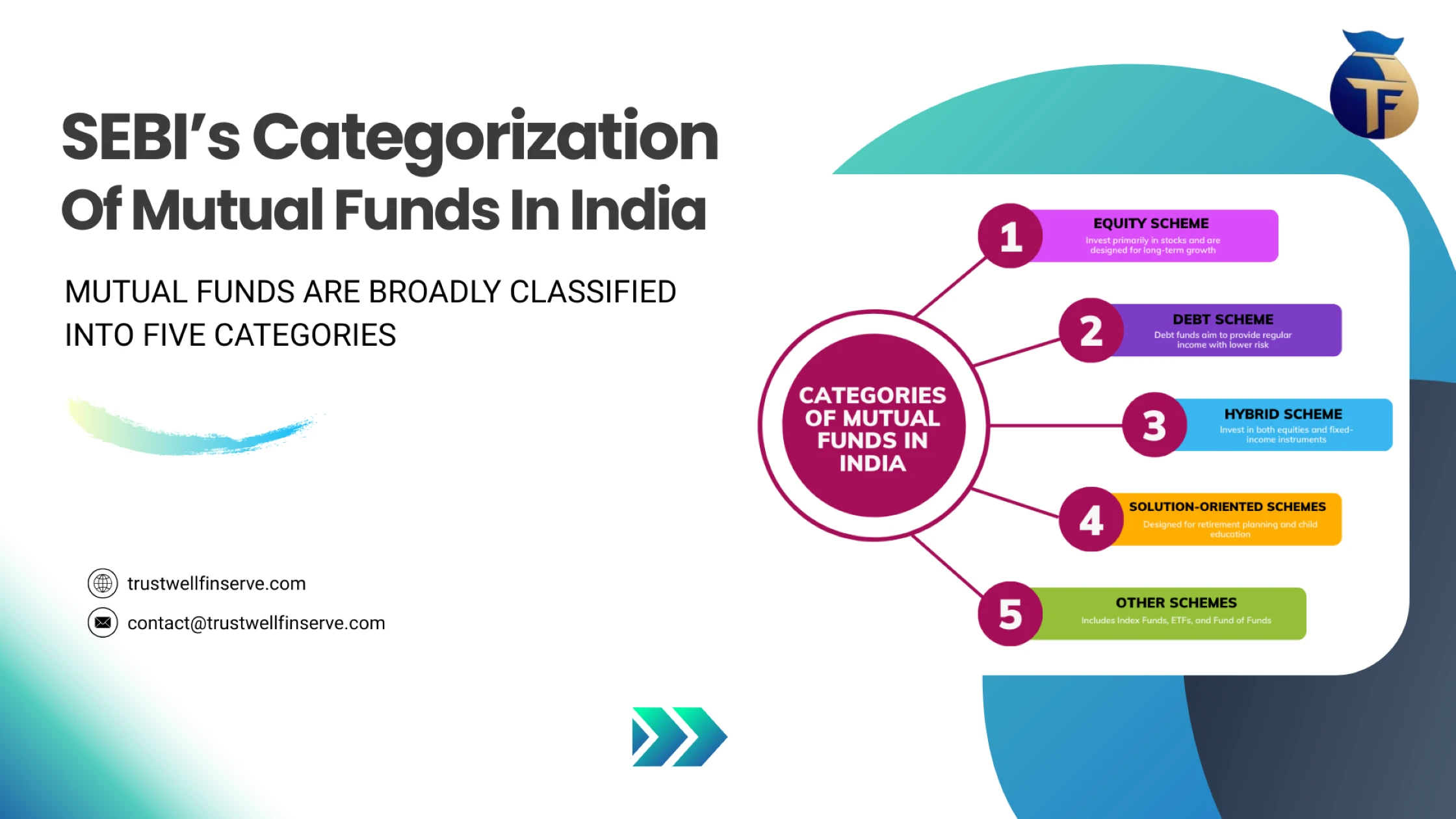
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds can be classified based on the types of assets they invest in and the fund’s investment approach:
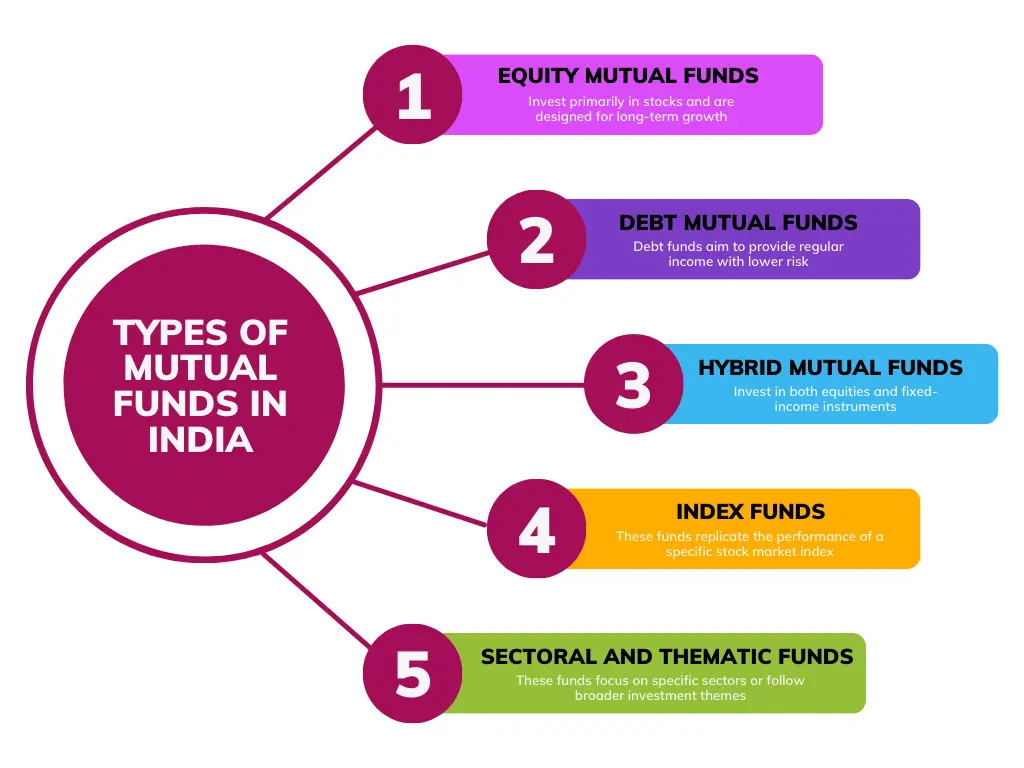
1. Equity Mutual Funds
Primarily invested in stocks, these funds aim for long-term Capital Appreciation. Sub-categories include:
2. Debt Mutual Funds
These invest in fixed-income instruments like government bonds, corporate bonds, and treasury bills. They offer lower risk and regular income. Common types include:
3. Hybrid Mutual Funds
Combining both equity and debt, Hybrid Funds offer a balanced risk-reward ratio. Examples include:
4. Index Funds
5. Sectoral and Thematic Funds
These funds concentrate on specific sectors like IT, healthcare, or finance, or broader themes such as ESG or infrastructure.
6. International or Global Funds
These invest in companies listed outside India, providing exposure to global markets and reducing reliance on the domestic economy.
🔗 Check the Latest Mutual Fund NAVs on Our Page
Benefits of Investing in Mutual Funds
1. Diversification
Spread your investment across various sectors, securities, and geographies, reducing overall risk.
2. Professional Management
Experienced fund managers research and manage your investments, saving you time and effort.
3. Low Investment Threshold
Start investing with relatively small amounts, making mutual funds accessible to a wider audience.
4. Liquidity
Most mutual funds, especially open-ended ones, offer easy entry and exit at the prevailing NAV.
5. Tax Efficiency
In India, equity mutual funds typically enjoy favorable tax treatment for long-term gains.
Risks Associated with Mutual Funds
1. Market Risk
Equity funds are subject to market Volatility, which can impact returns.
2. Credit Risk
In debt funds, there’s a risk of default if the issuer fails to repay interest or principal.
3. Interest Rate Risk
Rising interest rates can cause bond prices to fall, affecting the NAV of debt-oriented funds.
4. Liquidity Risk
Some funds may find it difficult to meet Redemption requests during market downturns, especially if they hold illiquid assets.
5. Management Risk
Actively managed funds rely heavily on the expertise of the Fund Manager. Poor decisions can lead to underperformance.
🔗 Also Read our full post on Risk Factors in Mutual Funds
Steps to Start Investing in Mutual Funds
1. Define Your Financial Goals
Determine whether your goals are short-term or long-term, such as buying a car or saving for retirement.
2. Pick the Right Fund
Choose a fund based on your risk appetite and Time Horizon. Equity for long-term growth, debt for stable returns.
3. Complete KYC Process
In India, completing the Know Your Customer (KYC) verification is mandatory before investing.
4. Select Investment Mode: Lump Sum or SIP
- Lump sum: Invest a large amount in one go.
- SIP (Systematic Investment Plan): Invest a fixed amount regularly to average out market volatility.
5. Track and Review
Regularly assess your fund’s performance and realign your portfolio as needed to stay in sync with your financial goals.
Other Important Considerations
1. Expense Ratio
This is the annual fee charged by the fund, which impacts your net returns. Lower expense ratios are generally preferable.
2. Exit Load
Some funds charge a fee if you Redeem your investment within a specified period. Always check the Exit Load before investing.
3. Taxation
Be aware of applicable taxes such as Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG) and Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG), which differ for equity and debt funds.
🔗 Also Read our full post on Understanding Portfolio Management Services in India
Final Thoughts
A solid understanding of mutual fund basics helps you make more confident and informed investment choices. These funds offer a convenient and efficient way to grow wealth, meet various financial goals, and access professional investment management. However, as with all investments, it’s important to assess your risk profile, financial needs, and time horizon before diving in. Regularly monitoring your investments and making adjustments when necessary will keep you on the path to financial success.
Disclaimer: The content on this blog is intended solely for educational purposes. All investment and financial planning strategies discussed are subject to market conditions and other factors beyond our control. Any securities or investments mentioned are not to be taken as recommendations or endorsements. Readers are encouraged to consult with a qualified Financial Advisor before making any investment decisions.